Wildfires are a global environmental challenge, escalating in frequency and intensity across the planet. These destructive events pose significant threats to human lives, livelihoods, and ecosystems worldwide. From the Amazon rainforest to the Arctic Circle, wildfires are ravaging landscapes, destroying homes, and displacing communities.
Climate change, with its rising temperatures and altered weather patterns, is a primary driver of this global trend, exacerbating drought conditions and creating more favorable conditions for fire ignition and spread. The consequences of these escalating wildfires are far-reaching, impacting air quality, biodiversity, and the global climate system.
The Southern California wildfires of 2025 (mainly the the Palisades Fire and the Eaton Fire), one of the most devastating wildfires in modern history, serves as a stark reminder of the risks posed by these events. In this article, we delve into what wildfires are, how they spread, the role of climate change, and actionable steps homeowners and industry leaders can take to reduce the physical and financial impact of wildfires.
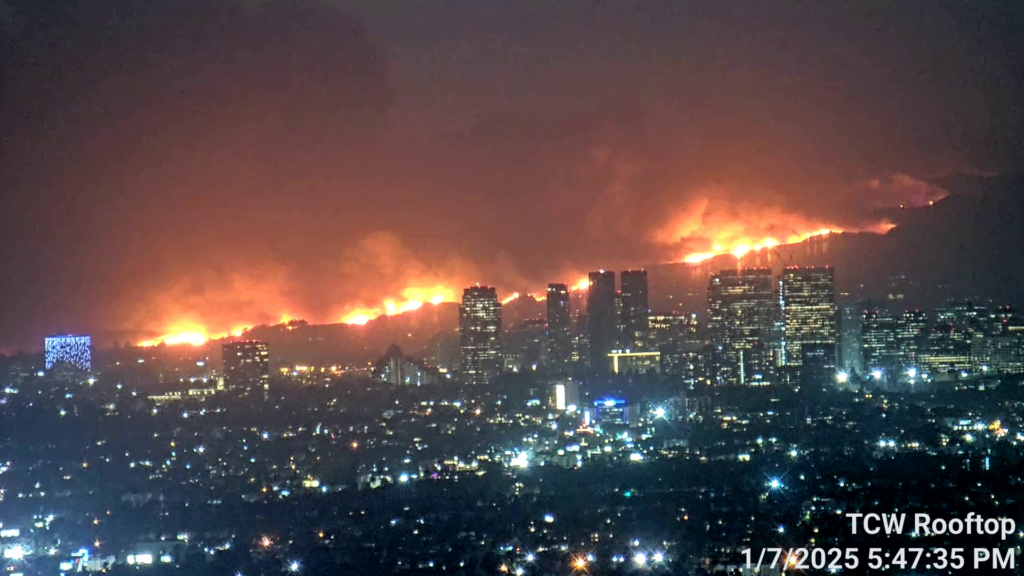

Source: By Toastt21 – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=157682430
What is a Wildfire?
A wildfire is an uncontrolled fire that ignites and spreads rapidly through vegetation, often consuming everything in its path, including structures and infrastructure. Wildfires are driven by a combination of factors, including dry conditions, high temperatures, strong winds, and abundant fuel sources like dry grasses, shrubs, and trees.
Wildfires can start from natural causes, such as lightning strikes, or human activities, including campfires, discarded cigarettes, electrical equipment failures, and arson. Once ignited, they can quickly escalate into massive infernos, particularly in areas where dry vegetation and strong winds are present.
How Do Wildfires Spread?
Wildfires spread through three primary mechanisms:
- Surface Fires: These fires burn low-lying vegetation, including grasses, leaf litter, and shrubs. Surface fires often act as the foundation for more severe fires.
- Crown Fires: These fires leap to the tops of trees, spreading rapidly through forest canopies. Crown fires are highly destructive and difficult to contain.
- Spot Fires: Embers carried by wind can ignite new fires ahead of the main blaze. These spot fires can complicate firefighting efforts and dramatically increase the fire’s spread.
Factors that influence the spread of wildfires include:
- Weather Conditions: High temperatures, low humidity, and strong winds accelerate fire spread.
- Fuel Load: Dense vegetation, dry debris, and dead trees provide ample fuel for fires.
- Topography: Fires move more quickly uphill, as rising heat ignites vegetation higher up the slope.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change has significantly exacerbated the conditions that fuel wildfires. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and shifting weather patterns have created a perfect storm for more frequent and intense fires. In the United States:
- Extended Droughts: Higher temperatures and reduced rainfall have dried out vegetation, turning it into tinder.
- Increased Wind Events: Stronger and more erratic winds spread embers farther and faster.
- Shrinking Snowpacks: Reduced snowmelt leads to lower water levels in reservoirs, affecting vegetation health and creating dry conditions.
Southern California wildfires of 2025
The Southern California wildfires of 2025 (the Palisades Fire and Eaton Fire) is a case study in the devastating effects of climate change. Fueled by record-breaking drought conditions and powerful Santa Ana winds, the fire consumed over 36,000 acres of land, destroyed more than 12,000 structures, and caused 11 fatalities (as of January 10th, 2025 – NBC News).
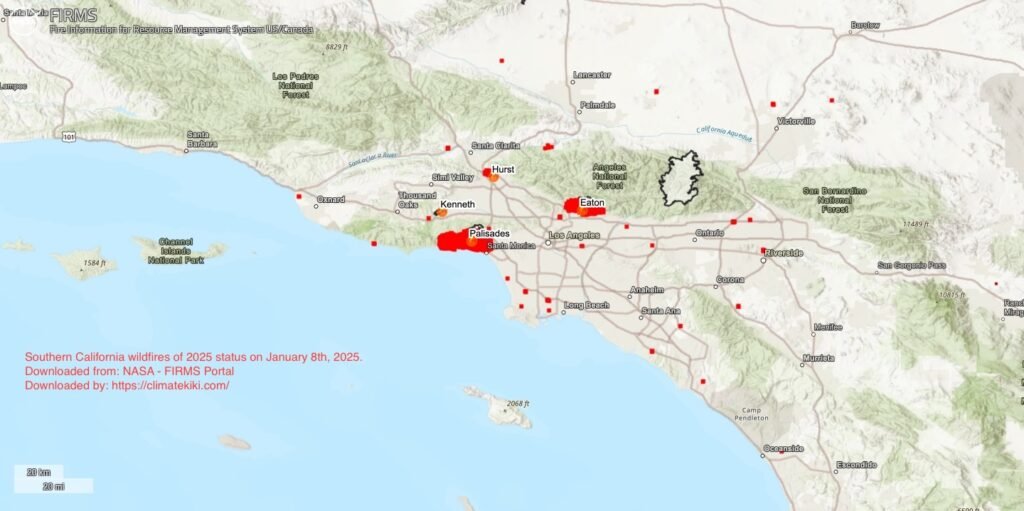
According to the investment bank JPMorgan, the projected economic losses from the ongoing wildfires have more than doubled since Wednesday (January 8th, 2025), reaching nearly $50 billion. Furthermore, estimates from AccuWeather suggest that these losses could climb even higher, potentially reaching as much as $135bn-$150 billion (source: BBC). In terms of insured losses, Southern California wildfires of 2025 (the Palisades Fire and Eaton Fire) is likely to be the costliest wildfire catastrophe so far, with losses reaching upto $20 billion (source: Reuters).
What Homeowners Can Do to Minimize Risk
Wildfires are unpredictable, but homeowners can take proactive steps to protect their properties and families. Here’s how:
1. Create Defensible Space
Defensible space is a critical buffer zone around your home that reduces the risk of fire reaching your property.
- Maintain a 30-foot zone free of flammable materials, such as dry leaves, woodpiles, and dead vegetation.
- Trim tree branches at least 10 feet away from chimneys and roofs.
- Regularly clean gutters and roofs to remove dry debris.
2. Use Fire-Resistant Building Materials
- Opt for fire-resistant roofing materials such as metal, tile, or asphalt shingles.
- Install dual-pane windows with tempered glass to reduce heat penetration.
- Seal gaps in siding, eaves, and vents to prevent embers from entering the home.
3. Landscape Smartly
- Plant fire-resistant vegetation like lavender, ice plants, or succulents.
- Use gravel, stone, or non-flammable mulch around your home instead of wood chips.
- Maintain a well-watered lawn and remove dead plants or trees.
4. Be Prepared for Evacuation
- Develop a wildfire evacuation plan and share it with your family.
- Prepare an emergency kit with essentials like food, water, medications, and important documents.
- Keep vehicles fueled and ready to leave at a moment’s notice.
What Industry Owners Can Do
Industries and businesses are not immune to wildfire risks. Proactive measures can save millions in damages and ensure business continuity.
1. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
- Identify fire-prone areas within and around your property.
- Ensure that all equipment is in good working order and does not pose a fire hazard.
- Store flammable materials in safe, designated areas away from vegetation.
2. Implement Fire Safety Plans
- Install fire suppression systems, including sprinklers and extinguishers.
- Train employees on fire safety protocols and evacuation procedures.
- Create firebreaks around industrial properties to slow the spread of fire.
3. Ensure Adequate Insurance Coverage
- Review your insurance policies to ensure they cover wildfire-related damages.
- Document all assets and keep digital backups for claims processing.
- Consider business interruption insurance to cover losses from downtime.
Actionable Tips to Reduce Financial and Physical Damage
- Stay Informed: Sign up for wildfire alerts through local and state authorities.
- Invest in Technology: Use weather-monitoring systems and fire detection tools to stay ahead of risks.
- Collaborate with Communities: Participate in local fire prevention initiatives and educate your community about wildfire risks.
- Backup Critical Data: Safeguard important personal and business information in secure, off-site locations or cloud storage.
- Prepare for Recovery: Have a post-fire recovery plan that includes contacting insurers, rebuilding, and supporting employees or family members.
Learning from the Southern California wildfires of 2025
The devastating Southern California wildfires of 2025 served as a stark reminder of the increasing threat of wildfires in the era of climate change. This event provided crucial insights for homeowners, businesses, and policymakers on how to mitigate future risks and enhance community resilience.
Key Takeaways:
- Defensible Space is Crucial: Properties with well-maintained defensible space, including cleared vegetation, fire-resistant landscaping, and non-combustible building materials, demonstrated significantly improved fire resistance. This highlights the importance of proactive measures by homeowners to protect their properties.
- Business Resilience is Paramount: Businesses with robust risk management strategies, such as emergency preparedness plans, insurance coverage for wildfire-related losses, and proactive communication with stakeholders, were better equipped to minimize financial and operational disruptions.
- Community-Wide Action is Essential: The Palisades Fire underscored the critical need for coordinated efforts across the community to address wildfire risks. This includes:
- Improved Land Management: Implementing effective fuel reduction programs, such as controlled burns and forest thinning, to reduce the risk of fire spread.
- Enhanced Building Codes: Strengthening building codes to mandate the use of fire-resistant materials in construction, particularly in high-fire-risk areas.
- Increased Investment in Firefighting Resources: Enhancing firefighting capabilities through improved technology, increased staffing, and better coordination between agencies.
- Public Education and Outreach: Raising public awareness about wildfire risks and promoting best practices for fire prevention and preparedness.
The Southern California wildfires of 2025 serves as a poignant reminder that wildfire risk is a shared responsibility. By learning from this event and implementing proactive measures at the individual, community, and policy levels, we can significantly reduce the devastating impacts of future wildfires and build more resilient communities.
Conclusion
Wildfires are an escalating threat in the United States, fueled by a combination of natural and human factors amplified by climate change. By understanding how wildfires spread and implementing preventative measures, homeowners and industry leaders can significantly reduce the risk of financial and physical losses.
The Southern California wildfires of 2025 serves as a sobering reminder of the devastating consequences of wildfires. However, it also offers valuable lessons on the importance of preparation and resilience. Protect your property, prepare for emergencies, and contribute to creating a safer, more fire-resilient community.
For more resources on wildfire prevention and preparedness, visit ready.gov/wildfires or contact your local fire department for assistance. Also, here is another article I wrote on the changes I did to make my home adaptable to climate change related risks.
Stay informed, stay safe!



